Want to learn how to trade CFDs? Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are financial instruments that allow traders to profit from the price movements of an underlying asset without actually owning it. Essentially, it’s a contract between a trader and a broker where they agree to exchange the difference in value of an asset from the start of the contract to its end. In this article, you will learn how to trade CFDs in 10 steps.
Table of contents:
- Choose a CFD Broker
- Open and Fund Your CFD Trading Account
- Choose the CFD Markets to Trade
- Choose to Buy or Sell
- Understand CFD Pricing
- Understand Margin and Leverage
- Set Your Stop-Loss Order
- Set Your Take-Profit Order
- Monitor Your CFD Trade and Adjust Your Position
- Closing the Trade
- Ready to practice CFD trading without putting in real money?
Choose a CFD Broker
Here are the 4 criteria to choose the right CFD broker:
Platform Usability
A user-friendly platform can significantly enhance your trading experience. Look for intuitive interfaces, easy navigation, and robust technical tools. For instance, ATFX provides traders with access to the Metatrader (MT4) platform, renowned for its user-centric design and advanced technical tools. The platform ensures traders can easily access, interpret, and act on market data. Download MT4 now!
Learn more about what is MT4 and how to use it.
Regulatory Compliance
Ensure your broker is regulated by a recognized financial authority. This offers protection against fraudulent practices, which also signifies their responsible handling of your funds. Consider ATFX for example; they abide by the directives of the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), a globally recognized regulator that ensures firms like ATFX operate correctly.

Customer Support
Reliable customer support can be invaluable, especially when you encounter issues. It’s essential to check for 24/5 availability, multiple contact methods, and responsiveness. ATFX, for example, prides itself on its dedicated support team, available around the clock and reachable through multiple channels, ensuring traders always have assistance when needed.
Educational Resources
Many brokers offer webinars, articles, and trading tutorials, which are especially beneficial for beginners. ATFX stands out in this regard, providing a comprehensive suite of educational resources, from insightful webinars to in-depth articles on trading strategies and market news, catering to both novice and experienced traders.
Learn more about the type of brokers – which one should you choose?
Open and Fund Your CFD Trading Account
ATFX is a globally recognized CFD broker reknown for its robust platform and diverse trading options. Here’s a step-by-step guide to set up your trading account:
Visit the ATFX Website
Start by navigating to the official ATFX website. This ensures you’re accessing a legitimate platform and not a phishing site.
Registration Process
Click on the ‘Open Account’ or ‘Register’ button, typically found at the top right corner.
Fill in the required personal details, including your name, email address, phone number, and country of residence.
Verification Process
To comply with financial regulations, ATFX requires identity verification. This usually involves uploading a copy of your government-issued ID and a recent utility bill or bank statement as proof of address.
Fund Your Trading Account
ATFX offers multiple deposit methods for your live trading account, including bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and e-wallets. Choose the one that’s most convenient for you.
Accessing the Trading Platform
Once registered and verified, you can log in to the ATFX trading platform. Familiarize yourself with its features, tools, and layout.
Many brokers, including ATFX, offer demo accounts, which allow you to practice trading strategies with virtual money before diving into real trades. Check out how to use demo account to improve trading .
Choose the CFD Markets to Trade
After getting the fundamental knowledge of how to trade CFDs, you can start to choose a CFD market to trade. The beauty of CFD trading lies in its versatility, allowing traders to engage with a plethora of markets. Here’s a breakdown to help you navigate your choices:
Engage with the dynamic world of currency pairs, capitalising on fluctuations between major and minor currencies. Check out the 10 most traded currencies.
Trade contracts based on individual company stocks from global stock exchanges. You may also be interested in trading Hong Kong’s CFD stocks.
Engage with broader market movements by trading the major global indices like the S&P 500, FTSE 100, or Nikkei 225. Check out the 6 reasons to trade indices CFDs .
Navigate the volatile yet lucrative world of digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and more. Check out the 10 Best CFDs.
Dive into assets like gold, oil, or agricultural products. Commodities can be a hedge against market volatility.
The image above shows a list of commodities CFDs that are offered at ATFX.
Choose to Buy or Sell
In CFD trading, you have the flexibility to either buy (go long) or sell (go short) on your chosen market, depending on your analysis and market predictions.
Going Long (Buying)
When you anticipate that the price of an asset will rise, you can choose to ‘buy’ or ‘go long’.
By doing so, you’re aiming to profit from a future increase in the asset’s price.
Going Short (Selling)
If you predict that the price of an asset will fall, you can ‘sell’ or ‘go short’. This allows you to potentially profit from declining markets.
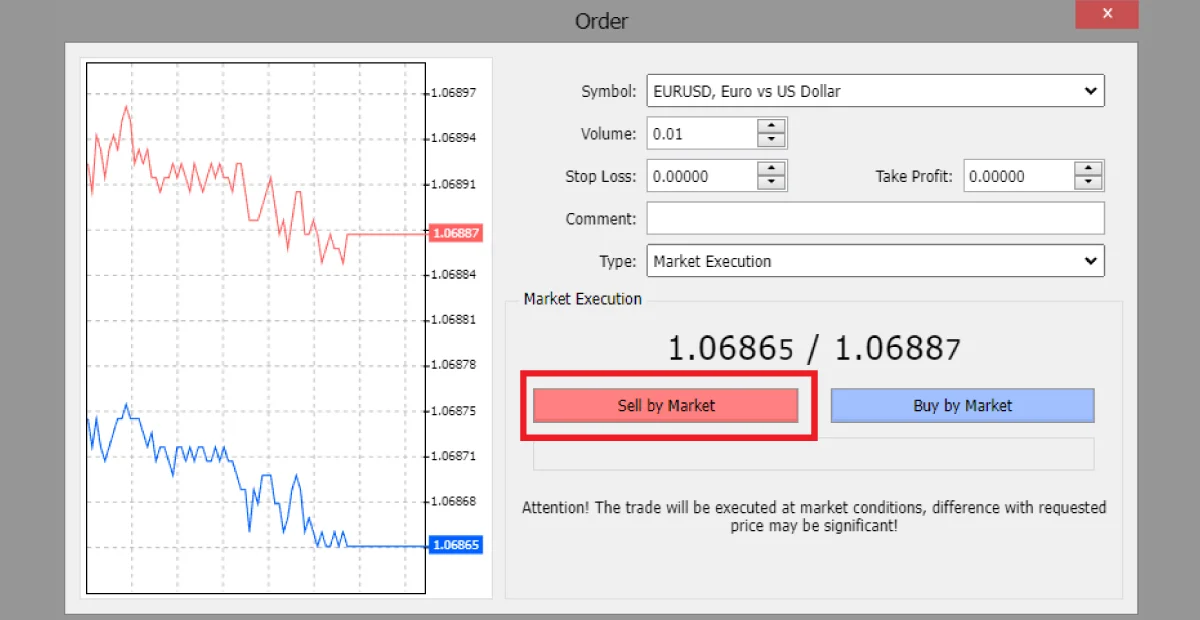
Factors Influencing Decisions
Market news, economic indicators, company performance, and geopolitical events can all influence whether a trader decides to go long or short.
Understand CFD Pricing
CFD pricing is a fundamental concept that every trader should grasp. It’s determined by various factors and can influence your trading decisions and potential profits or losses.
Bid and Ask Prices
The bid price is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for an asset, while the ask price is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
The difference between these two prices is known as the spread. The spread represents the broker’s profit (aside from any commission or fees), as traders will buy at the bid price and sell at the ask price.

Example: If the bid price for a stock CFD is $100 and the ask price is $102, the spread is $2.
Factors Influencing CFD Prices
Underlying Market Price: The primary factor. If the price of the underlying asset (e.g., a stock or commodity) rises, the CFD price will typically rise as well.
Market Volatility: During times of high volatility, spreads might widen.
Liquidity: In highly liquid markets, spreads tend to be narrower.
Supply and Demand: As with any market, shifts in supply and demand can influence prices.
Cost Associated with CFD Trading
Holding Costs: If you keep a position open overnight, you might incur a holding cost, which can be a charge or a credit.
Commission: Some brokers charge a commission on CFD trades.
Understand Margin and Leverage
Margin and leverage are integral to CFD trading, allowing traders to maximize their market exposure using a relatively small initial deposit. However, they also amplify risks, making it essential to understand their mechanics. Learn more about Risk and Reward Ratio | 5 Risk management techniques.
What is Margin?
Margin is the initial deposit required to open a CFD position. It’s a fraction of the full value of your trade.
There are 2 main types of margin: Initial Margin (the initial deposit to open a position) and Maintenance Margin (the minimum amount required to keep a position open).
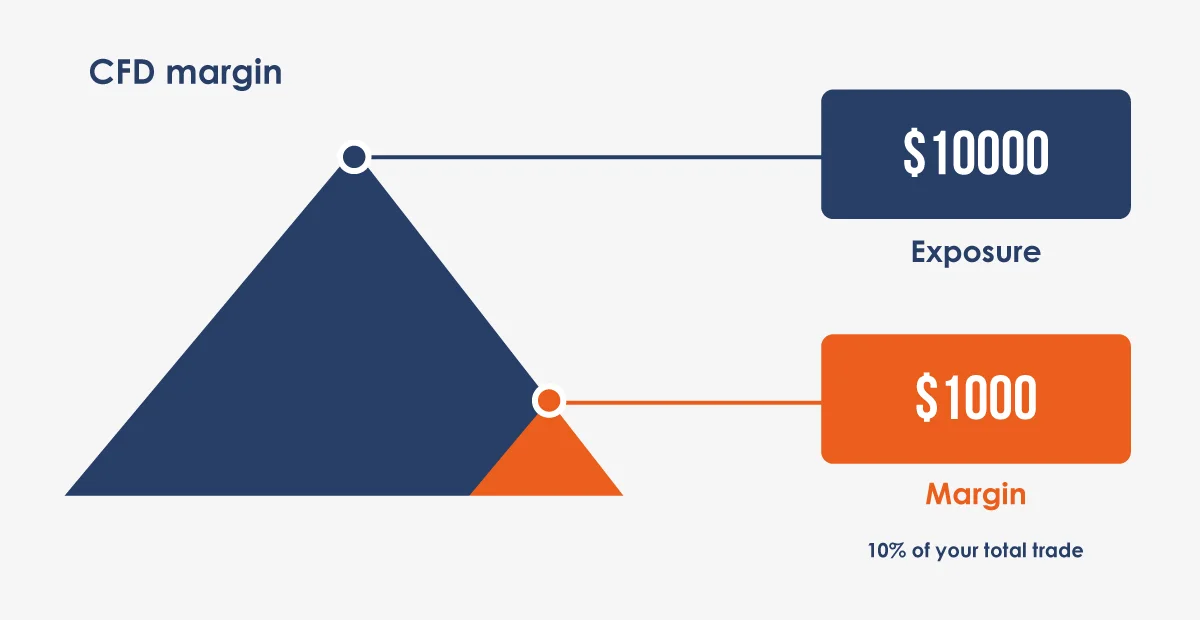
Example: If you want to open a CFD position equivalent to $10,000 and the broker requires a 10% margin, you’d need to deposit $1,000.
The Power of Leverage
Leverage allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of money. It’s expressed as a ratio, such as 10:1, meaning you can control a position 10 times larger than the amount you deposited.
While leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses.
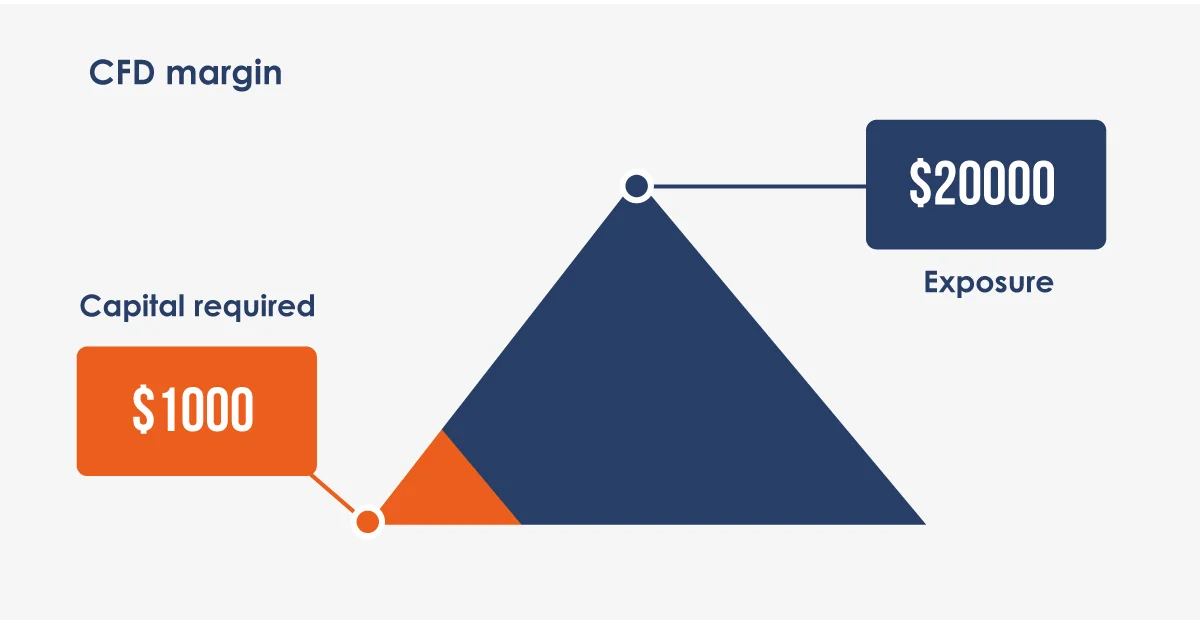
Example: With a deposit of $1,000 and leverage of 20:1, you can control a position worth $20,000. If the market moves 5% in your favour, you will gain $1,000 (a 100% return on your deposit). However, if it moves 5% against you, you will lose your entire deposit.
Margin Calls
If your account balance falls below the maintenance margin due to adverse market movements, the broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds.
Failing to meet a margin call might result in the broker closing your positions to limit any further losses.
Example: Imagine you held a CFD position with a maintenance margin of $500. Due to market shifts, your account balance decreased to $450, prompting a margin call. To maintain your position, you had to add more funds to your account.
Set Your Stop-Loss Order
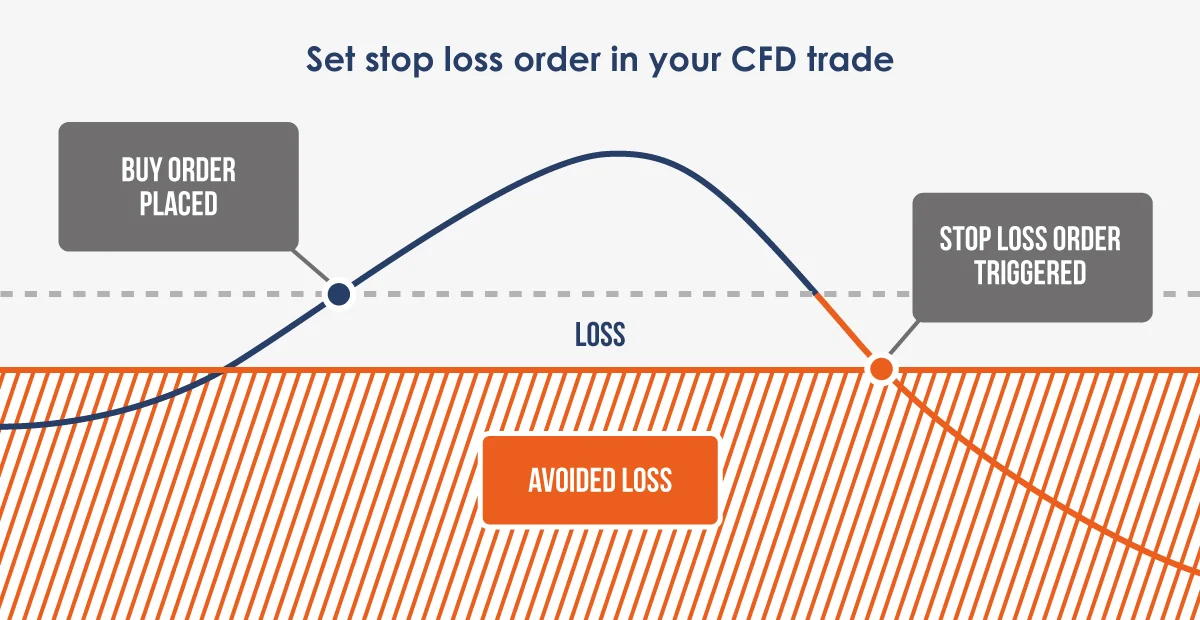
A stop-loss is a crucial risk management tool in CFD trading. It automatically closes your trades when the market moves against you to a specified level, helping to limit potential losses.
Importance of a Stop-Loss Order
Markets can be unpredictable. A stop-loss ensures you don’t hold onto a losing position for too long, protecting your capital. It provides peace of mind, especially when you can’t constantly monitor your trades.
How to Determine Stop-Loss Levels
The stop-loss level should be based on your risk tolerance and market analysis.
Some traders use technical indicators, like support and resistance levels, to set their stop-loss orders.
Example: Imagine you purchased a stock CFD at $100. Using technical analysis, you pinpointed a support level at $95. To safeguard against potential losses, you positioned your stop-loss order just beneath this level at $94.50.
Types of Stop-Loss Orders
Regular Stop-Loss: Triggers once the market reaches the set price.
Trailing Stop-Loss: Adjusts with the market. If the market moves favourably, the stop-loss moves with it, locking in profits. But if the market moves against you, the stop-loss order remains at its last price level.
Guaranteed Stop-Loss: For a small premium, some brokers offer a guaranteed stop-loss order, ensuring your position closes at the exact level you set, regardless of the market gapping higher or lower.
Example: You established a trailing stop-loss for your forex CFD. As the currency pair ascended, your stop-loss level adjusted upwards in tandem, ensuring you secured profits when the market trend eventually shifted.
Set Your Take-Profit-Order
A take-profit order is a predetermined level at which your trade will automatically close, locking in your profits. It’s an essential tool to ensure you capitalize on favourable market movements.
Importance of a Take-Profits Order
Markets can reverse direction quickly. A take-profit order ensures you secure your gains before the trend changes.
It helps in maintaining trading discipline, preventing greed from making you hold onto a position for too long.
Determining the Take-Profit Level
The take-profit level should be based on your desired profit target and market analysis.
Many traders use technical indicators, such as resistance levels or Fibonacci retracements, to set their take-profit orders.
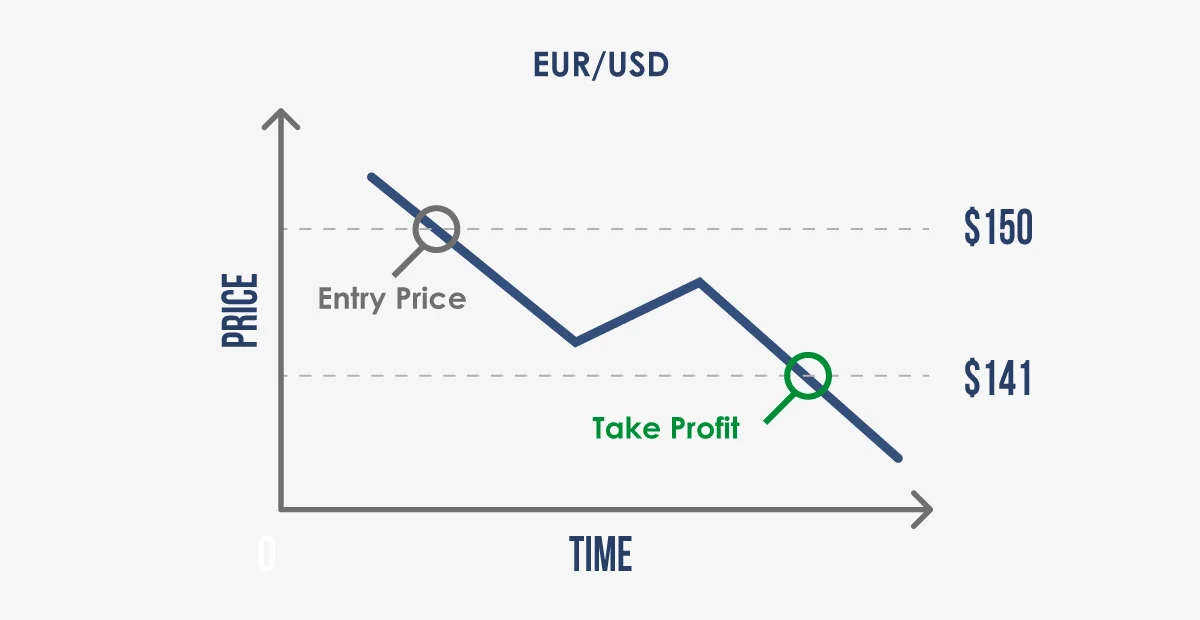
Example: Suppose you decided to short a stock CFD at $150. Through technical analysis, you identified a support level of $140. To maximize potential profits, you placed your take-profit slightly above this mark at $141.
Flexibility with Take-Profit Orders
While it’s essential to have a profit target, it’s equally crucial to be flexible. If market conditions change or new information becomes available, adjust your take-profit order accordingly.
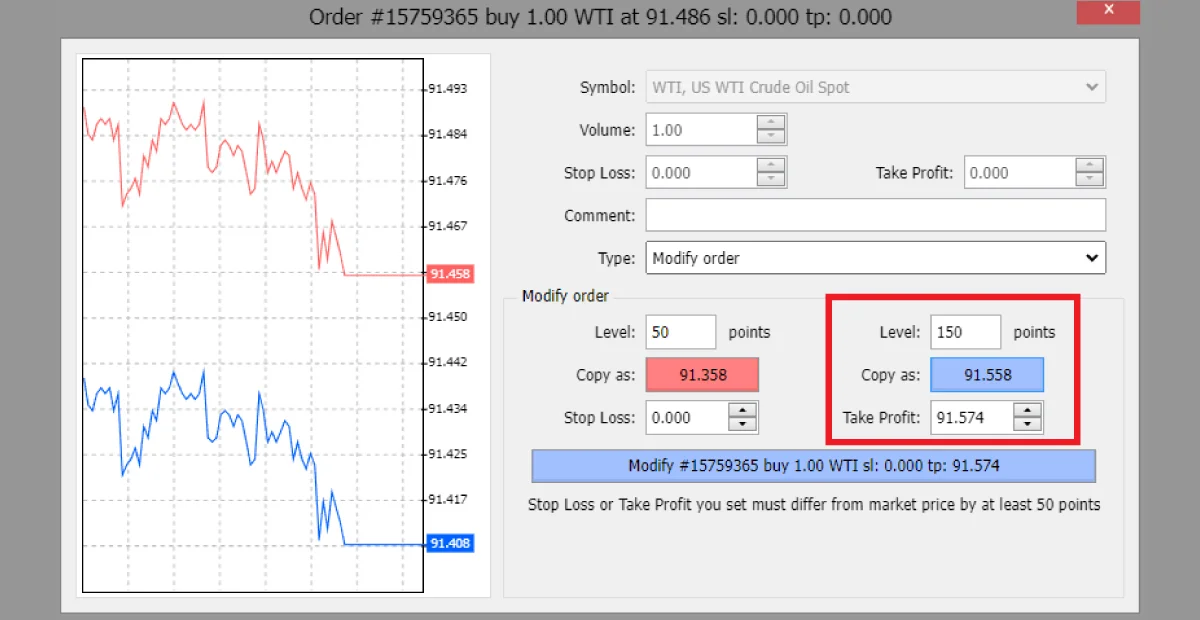
Example: Initially, you set a take-profit for your forex CFD aiming for a 100-pip gain. Yet, following a significant economic update, you foresaw a more favourable market swing and adjusted your take-profit to target a 150-pip profit.
Monitor Your CFD Trade and Adjust Your Position
Once you’ve entered a CFD trade, the journey isn’t over. Actively monitoring and adjusting your position based on market dynamics is essential for optimising trading outcomes.
The Importance of Monitoring
Markets is ever-changing and influenced by numerous factors. By regularly checking your trades, you ensure you’re not blindsided by sudden market shifts.
Monitoring helps you make informed decisions, be it adjusting stop-loss/take-profit levels or closing a position early.
Example: Imagine you have a long position in a tech stock CFD. After keeping an eye on the news, you discover a sudden regulatory challenge the company is facing. Promptly adjusting your position can help mitigate potential losses.
Tools for Monitoring
Price Alerts: Set up notifications for when an asset hits a specific price, ensuring you don’t miss crucial market movements.
Technical Analysis Tools: Utilise MT4 indicators and charts to track price movements and anticipate future trends.
Economic Calendars: Stay in the loop with significant economic events that could impact your trades by monitoring the economic calendar. Check out our MT4 economic calendar .
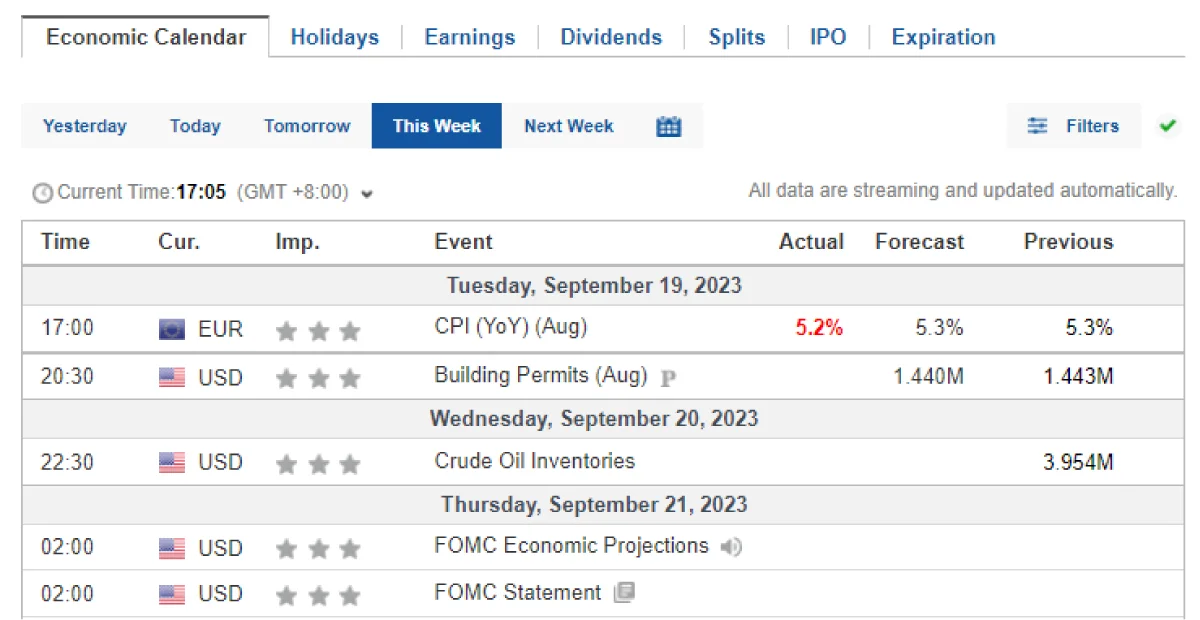
Example: Suppose you use an economic calendar to monitor major announcements. When a central bank alters interest rates, you’re prepared and adjust your forex CFD trades accordingly.
Adjusting Your Position
Depending on market movements and your analysis, there might be a need to modify your trade. This could involve shifting your stop-loss or take-profit levels or increasing your position if the market is favourable.
Closing the Trade
Closing a CFD trade is a crucial step, marking the end of your position and the realization of any profits or losses. It’s essential to understand when and how to close a trade effectively.
Reason to Close a Trade
Profit Target Reached: If the market moves in your favour and reaches your take-profit level, you might decide to close the trade and lock in your gains.
Stop-Loss Triggered: To prevent further losses, your trade might automatically close if it hits your predetermined stop-loss level.
Market Analysis: Based on new data or market analysis, you might believe that the current trend is about to reverse.
Example: Imagine you held a long position in a tech stock CFD. After keeping abreast of the news, you discovered an unexpected regulatory challenge the company was facing. Without hesitation, you quickly modified your position to minimise potential losses.
Methods to Close a Trade
Manual Closure: You can close a trade manually via your trading platform when you believe it’s the right time.
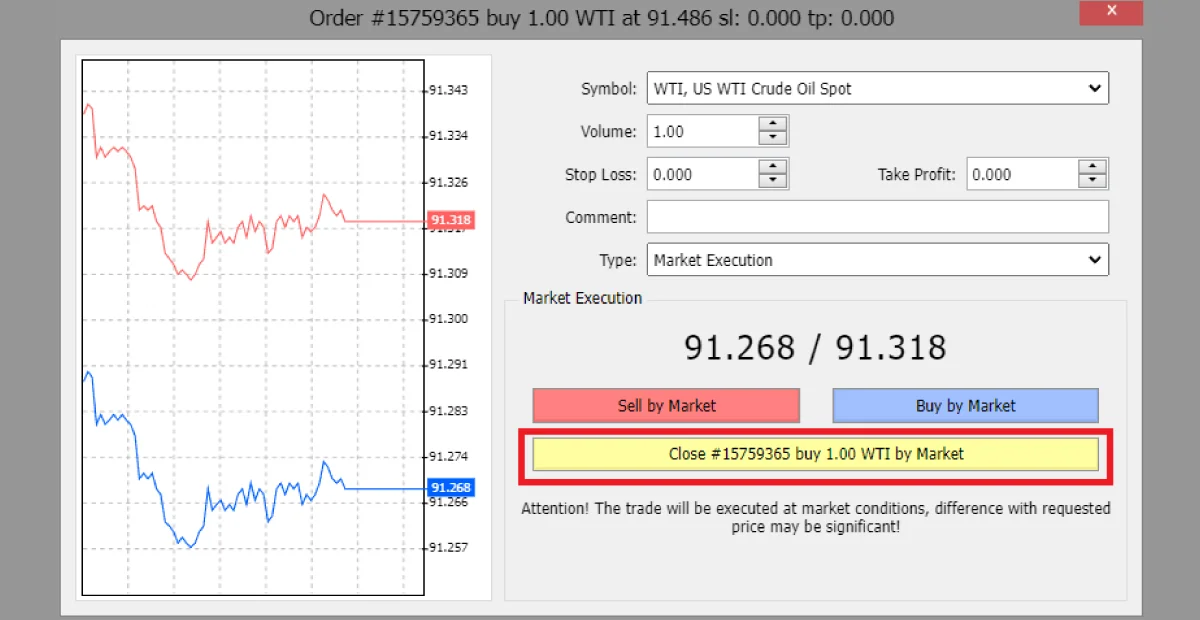
The image above shows closing the order manually by pressing the close order button.
Automatic Closure: Setting stop-loss or take-profit levels can result in the automatic closure of a trade when these levels are reached.
Example: You utilised an economic calendar to stay updated on significant events. When the central bank announced a shift in interest rates, you were ready and closed your forex CFD trades in response.
The Impact of Closing a Trade
Once a trade is closed, any profits or losses are realised, and the funds are adjusted in your trading account.
It’s essential to review closed trades, analyse what went right or wrong, to refine your trading strategy.
Example: Observing a steady upward trend in your commodity CFD trade, you chose to extend your take-profit level, targeting an even greater profit.
Ready to practice CFD trading without putting in real money?
Are you ready to start trading CFDs after learning how to trade CFDs in 10 steps? Register for a free demo account with ATFX to gain hands-on experience in the trading realm. ATFX offers numerous other CFD trading markets, with our user-friendly MT4 platform to experiment with various trading strategies. Register for your free demo trading account today! After learning how to trade CFDs with the demo account, you can upgrade to a live account for real-time trading immediately!




