What is EUR/USD
EURUSD is the exchange rate value of one euro to US dollars. It indicates how many US dollars (USD) are needed to purchase one euro (EUR). For example, if the EUR/USD rate is 1.50, it means that 1 euro can be exchanged for 1.50 US dollars.
EURUSD pair is the most traded currency pair globally, making up a major portion of the forex market. EURUSD has more liquidity, tighter spreads, and greater market depth compared to GBP/USD and USD/JPY.
Examples of the EUR/USD Exchange Rate
For example, if a European company sells goods worth €10,000 to a US company, and the EUR/USD rate is 1.20, the US company will need to pay $12,000 (10,000 x 1.20) for the goods.
On the other hand, if the rate drops to 1.10, the same goods would cost the US company $11,000. This demonstrates the direct impact of exchange rates on international trade.
Why is the EUR/USD Structured with the Euro as the Base Currency?
EUR/USD currency pairs use euro as the base currency, and the US dollar is the quoted currency. This structure is somewhat unique because, in most currency pairs, the US dollar typically serves as the base currency. The EURUSD shows the euro’s important role in the global economy, highlighting the Eurozone’s economic power.
The Differences Between EUR/USD and USD/EUR
EUR/USD shows the dollars needed to buy one euro, while USD/EUR shows the euros needed to buy one dollar. For example, if EUR/USD is 1.20, then USD/EUR is 0.8333 (1/1.20).
This inverse relationship impacts traders’ strategies and economic interpretations, highlighting the need to understand which currency is the base and which is the quote.
| Feature | EUR/USD | USD/EUR |
| Base Currency | Euro (EUR) | US Dollar (USD) |
| Quote Currency | US Dollar (USD) | Euro (EUR) |
| Interpretation | Number of US dollars per €1 euro | Number of euros per $1 US dollar |
| Typical Quotation | $1.09 (€1 euro = $1.09 dollars)* | €0.92 ($1 dollar =€ 0.92 euros)* |
| Usage in Forex Markets | More common and widely used | Less common, often calculated for comparison |
| Implications for Traders | Direct impact on euro value vs. dollar | Inverse impact on dollar value vs. euro |
| Economic Strength | Reflects Eurozone economic strength | Reflects US economic strength |
*For illustration purposes only. To access the EUR/USD rate in the trading platform, please log in to the client portal.
Major Factors that Impact the Euro to Dollar Exchange Rate
- Interest rate differences set by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the Federal Reserve (Fed) can drive demand for euros or dollars.
- Economic indicators like GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation figures from the Eurozone and the US can significantly impact the exchange rate.
- Geopolitical events like political stability, trade agreements, and international conflicts can change market perceptions and currency values.
- Economic events like changes in monetary policy, fiscal stimulus, and crises can significantly impact the EUR/USD exchange rate.
The Role of International Trade Between Europe and the USA
A trade surplus in the Eurozone means higher demand for euros, potentially strengthening the EUR/USD rate. Conversely, a trade deficit could weaken the euro against the dollar.
History of the Euro to Dollar
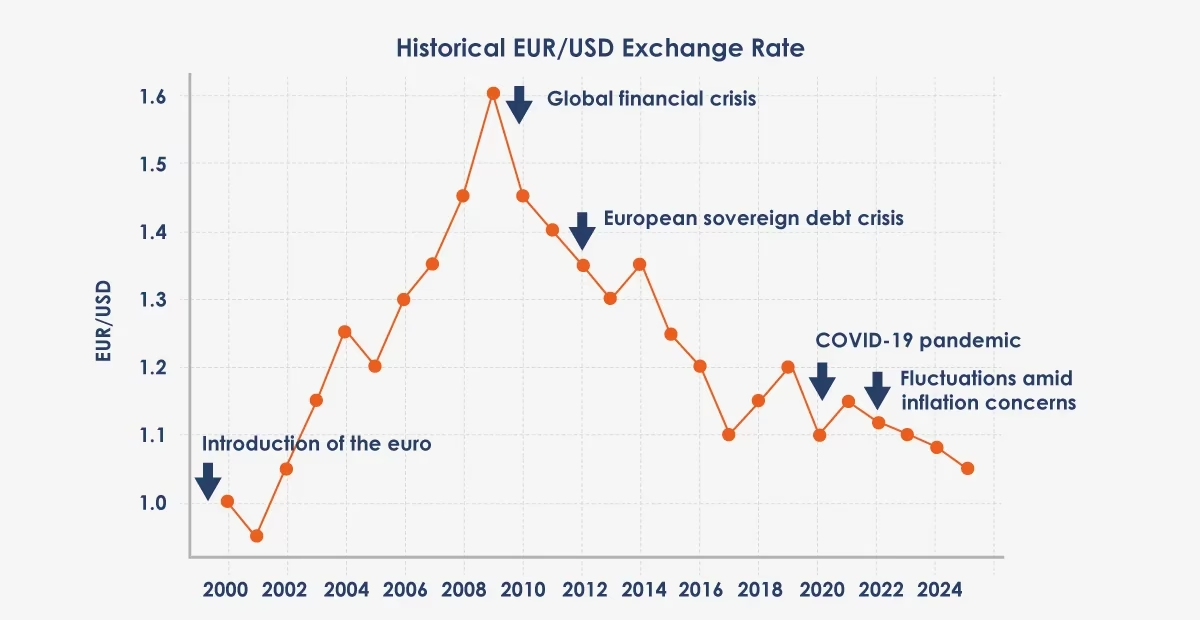
EUR/USD currency pair has changed significantly since the euro was introduced on 1 January 1999. Initially, the euro was valued lower than the dollar, but it gained strength, peaking at around 1.60 in 2008.
These changes reflect the economic conditions and monetary policies of the Eurozone and the US. Historical analysis shows that the EUR/USD exchange rate follows patterns influenced by macroeconomic trends, such as shifts in economic growth and policy differences between the ECB and the Fed.
The relationship between the euro and the dollar has evolved through various economic cycles, including the 2008 global financial crisis, the European sovereign debt crisis, and uncertainties due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Each event has left a distinct mark on the EUR/USD exchange rate live chart, as shown on the live chart.
Milestones:
- 1999: Introduction of the euro, initially valued lower than the dollar.
- 2008: Euro peaks at around 1.60 USD.
- 2008: Global financial crisis impacts EUR/USD exchange rate.
- 2010-2012: European sovereign debt crisis influences the exchange rate.
- 2020: COVID-19 pandemic creates economic uncertainties affecting EUR/USD.
- 2022-2024: EUR/USD pair fluctuated amid persistent inflation concerns, shifting interest rate differentials, and evolving economic conditions.
Why is the EUR/USD Pair Considered the Most Traded Currency Pair?
The EUR/USD currency pair is the most traded due to the Eurozone’s economic size. Its high liquidity allows traders to enter and exit positions with minimal slippage, making EUR/USD an attractive option for forex traders.
The EUR/USD currency pair’s high liquidity allows for diverse trading strategies, including spot trading, Contracts for Difference (CFDs), and spread betting.
EUR/USD Trading Hours
EUR/USD operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with forex market trading sessions in Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. The EURUSD best trading times are during the London and New York overlap (12:00 PM to 4:00 PM GMT), offering high liquidity and volatility, making it ideal for short-term trades due to significant price movements and opportunities.



