What is Forex Trading
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading or currency trading, is the global marketplace for exchanging national currencies against one another. As one of the largest financial markets in the world, it operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and boasts a daily trading volume that exceeds $6 trillion. This market is essential for international trade, investments, and global economic stability.
Forex Currency Pairs and Quotes
In Forex trading, currencies are quoted in pairs, and each pair is associated with a two-part price: the bid and the ask. The bid price represents the maximum amount a buyer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price represents the minimum amount a seller is willing to accept. Currency pairs are categorised into three types:
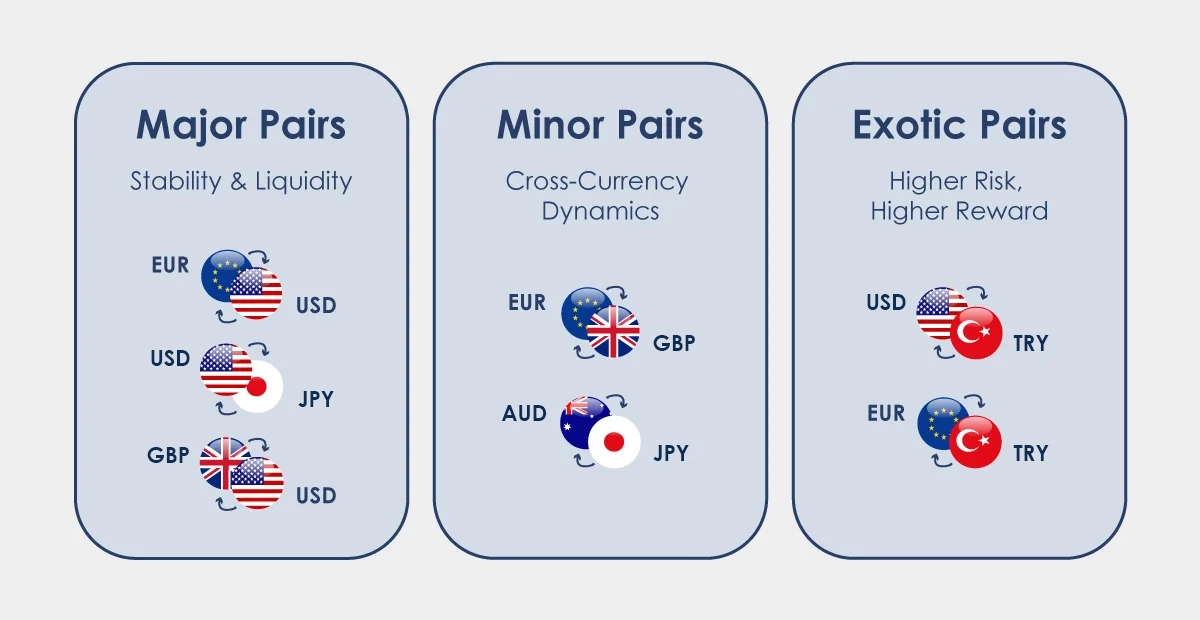
Major Pairs
Major pairs involve the most traded currencies globally, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. Major pairs typically offer high liquidity and tight spreads.
Minor Pairs
Minor pairs consist of currencies from major economies but do not involve the US dollar. Examples include EUR/GBP, AUD/JPY, and CAD/CHF. Minor pairs often have wider spreads compared to major pairs.
Exotic Pairs
Exotic pairs involve one major currency and one currency from a smaller or emerging market, such as USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African rand), USD/CNH (US Dollar/Chinese Renminbi Offshore) or EUR/HUF (Euro/Hungarian Forint). Exotic pairs tend to be less liquid and more volatile.
Understanding Forex Trading Base and Quote Currency
Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another. These transactions occur in currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD or GBP/JPY, where the first currency listed is the base currency and the second is the quote currency. The goal of forex trading is to profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates between these two currencies.

For instance, if a trader believes the euro will strengthen against the US dollar, they might buy the EUR/USD pair, hoping to sell it later at a higher price. Conversely, if they expect the euro to weaken, they would sell the pair, aiming to repurchase it at a lower price.
What Are Pips in Forex Trading?
A pip, which stands for “percentage in point,” is the smallest price movement that can occur in a currency pair within the Forex market. Typically, for most currency pairs, one pip equals 0.0001. For example, if the EUR/USD pair moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, it has increased by one pip. Pips are fundamental in Forex trading as they help calculate both profits and losses, representing the incremental changes in exchange rates that traders aim to capitalise on.

What Is the Spread in Forex Trading?
The spread in forex trading refers to the difference between the bid (selling) price and the ask (buying) price of a currency pair. The spread is essentially the cost of executing a trade and is a primary way brokers earn money. For instance, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1050 and the ask price is 1.1100, the spread is 50 pips. In markets with high liquidity, such as major currency pairs, spreads are typically narrower, while less liquid markets, like exotic currency pairs, often have wider spreads.

What Is Lot Size in Forex Trading?
Lot size in Forex trading determines the volume or amount of currency involved in a trade. It is a crucial factor in calculating a trade’s potential profit or loss. Different lot sizes include:
| Lot Type | Lot Size | Units of Base Currency | Pip Value (USD) |
| Standard Lot | 1.0 | 100,000 units | $10 |
| Mini Lot | 0.1 | 10,000 units | $1 |
| Micro Lot | 0.01 | 1,000 units | $0.10 |
| Nano Lot | 0.001 | 100 units | $0.01 |
Standard Lot
Standard lot is equivalent to 100,000 units of the base currency. For example, one standard lot in the EUR/USD pair involves trading 100,000 euros.
Mini Lot
Mini lot is equal to 10,000 units of the base currency, which is one-tenth of a standard lot. This size is commonly used by traders with smaller accounts.
Micro Lot
Micro lot consists of 1,000 units of the base currency, one-tenth of a mini lot, often used by beginners or those minimising risk.
Nano Lot
Nano Lot comprises 100 units of the base currency and is ideal for extremely cautious traders who prefer minimal trade amounts.
Understanding lot size is vital for effective risk management in Forex trading, as it directly influences the financial impact of each pip movement.
The Structure of the Forex Market
The forex market is unique in its decentralised nature. Unlike stock markets, which are typically centralised on a single exchange, forex trading occurs over-the-counter (OTC). This means that transactions are conducted directly between parties, usually through electronic trading platforms or via telephone, without a centralised exchange.
The forex market is composed of several key players:
- Central Banks: Central banks play a pivotal role in the forex market by managing currency reserves, setting interest rates, and intervening in the market to stabilise their currency.
- Commercial Banks: These institutions conduct large volumes of currency transactions for clients and for their trading accounts. They also provide liquidity to the market.
- Hedge Funds and Investment Managers: These entities trade significant amounts of currency to hedge against risk or for speculative purposes.
- Corporations: Multinational companies engage in forex trading to facilitate international trade, such as converting revenue from overseas sales.
- Retail Traders: With the advent of online trading platforms, individual traders now have access to the forex market. Although retail traders account for a smaller portion of the overall market, their influence has grown significantly in recent years.
How Do Forex Market Hours Affect Trading?
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to its global nature. This continuous operation is possible because as financial centres in different parts of the world open and close, the market remains active, with trading sessions in Asia, Europe, and North America. This 24/5 structure allows traders to react promptly to global events and economic developments, regardless of their location, ensuring that trading opportunities are available almost around the clock.
Factors Influencing Forex Prices
Currency prices in the forex market are influenced by various factors, which traders must consider when making decisions:
- Interest Rates: Central banks’ interest rate policies significantly drive currency prices. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the currency.
- Economic Indicators: Economic data such as GDP growth, employment figures, and inflation rates can impact currency values. Positive economic news typically strengthens a currency, while negative data can weaken it.
- Political Stability: A country’s political environment can influence its currency. Stable governments tend to attract investment, while political uncertainty or unrest can lead to currency depreciation.
- Market Sentiment: Traders’ perceptions and expectations can also drive currency prices. If investors believe a currency will strengthen, they may buy it, increasing its value.
- Global Events: Events such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics can have immediate and often unpredictable effects on currency prices.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading can be conducted through various methods, depending on the trader’s goals and risk tolerance. Following are the types of forex trades.
Spot Market
The spot market is where currencies are bought and sold for immediate delivery. Prices are determined by supply and demand in real-time, and trades are usually settled within two business days. The spot market is the most common form of forex trading.
Forward Market
In the forward market, traders enter into contracts to buy or sell a currency at a future date, at a predetermined price. This method is often used by companies and financial institutions to hedge against currency risk.
Futures Market
Similar to the forward market, the futures market involves contracts to buy or sell currency at a future date. However, unlike forward contracts, futures contracts are standardised and traded on exchanges. Futures trading is often used by speculators looking to profit from anticipated currency movements.
Options Market
The options market allows traders to buy or sell a currency at a specific price before a certain date, but they are not obligated to do so. This gives traders the flexibility to hedge against potential losses while limiting their risk.
CFDs (Contracts for Difference)
CFDs are derivative products that allow traders to speculate on currency price movements without owning the underlying asset. CFD trading can offer high leverage, meaning traders can control a large position with a relatively small investment, but it also comes with higher risk.
Read more about Spot vs Futures vs Contract-For-Difference
What Is Leverage in Forex Trading?
Leverage is a key feature of forex trading, allowing traders to control larger positions than they would with their capital alone. For example, with a leverage ratio of 50:1, a trader can control a $50,000 position with just $1,000 of their capital. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
What Is Margin in Forex Trading?
Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is essentially a good-faith deposit that the broker holds to cover potential losses. If a trader’s position moves against them, they may receive a margin call, requiring them to deposit additional funds to maintain their position.
How to Manage Risk in Forex Trading?
Risk management is a crucial aspect of forex trading and successful traders employ various strategies to protect their capital and limit losses through the following steps.
Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically closes a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level. This helps traders minimise losses if the market moves against them.
Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss orders are take-profit orders that automatically close a trade when the price reaches a specific profit target. This allows traders to lock in gains and avoid the temptation of holding onto a position for too long.
Position Sizing
Traders carefully consider the size of their positions relative to their overall capital. By risking only a small percentage of their account on each trade, they can minimise the impact of any single loss.
Diversification
Diversification can reduce risk in forex trading. By trading multiple currency pairs, traders can spread their risk across different markets and reduce their exposure to any one currency.
How to Get Started in Forex Trading with ATFX?
We offer the popular MetaTrader 4 (MT4) platform, which you can fully customize. This popular trading platform is well respected and has many features and benefits.
You have all the features and benefits of MT4 and our complementary tools, which offer you a great trading experience when combined. These include Trading Central, Market News, and Autochartist, to name a few. Learn how to use MT4.


