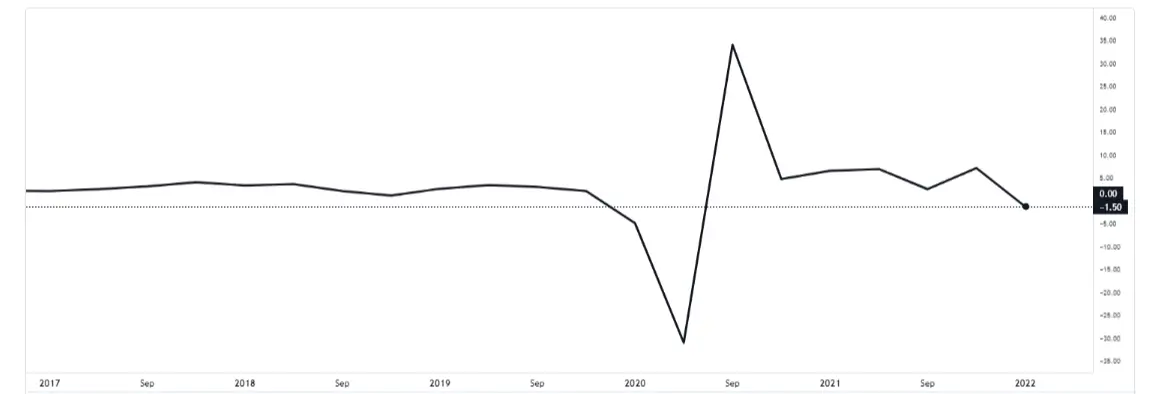
Tonight, crucial economic data about the US first-quarter real GDP growth final annualised rate will be released. The previous value was -1.50%, and the expected value was -1.40%. Many experts predict that the US economy may fall into recession as the country faces multiple macro challenges that cannot be quickly resolved. Hence, investors are particularly concerned about the final GDP data during the first quarter.
At the same time, the forecasts for the second-quarter GDP growth of the United States are not optimistic. The Atlanta United Bank forecast shows that the domestic GDP growth in the second quarter may be zero, indicating that the economy is on the verge of a recession. If the US GDP growth is negative for two consecutive quarters, it will suggest that the country’s economy is in recession.
Goldman Sachs kept its US GDP growth forecast unchanged at 2.8 percent in the second quarter but lowered its growth forecast from the third quarter of 2022 to the first quarter of 2023. There is a belief that the US economy is more likely to fall into recession in the next two years, with the cumulative probability of such an outcome rising to 48%.
The latest data from Atlanta United Bank’s GDPNow forecast model was available on June 7. The annual growth rate of the United States gross domestic product (GDP) in Q2 was revised from 1.3% to 0.9%. The forecasts indicate that the US economy is relatively close to recession after a 1.5% decline in the first quarter.
The upcoming GDP data will be crucial for the US dollar’s trend. Despite speculation of a 0.75% interest rate hike next month, the market seems to believe a 0.50% rate hike is more likely, after which interest rates will peak at around 3.5% in March 2023. Suppose the US Federal Reserve gradually reduces or terminates future rate hikes as the market predicts. In that case, such a move would be detrimental to the US dollar’s subsequent performance.
Suppose data shows the US economy is likely to enter a recession and register zero or negative growth. In such a scenario, aggressive rate hikes will be even lower because the Fed will not choose to sacrifice economic growth to raise interest rates significantly. As a result, the magnitude of future rate hikes may be limited. Therefore, the recent downturn in financial data will also be a negative factor for the US dollar trend. Conversely, if US economic data exceeds market expectations, the Fed is likely to decide to raise interest rates more firmly, which could help the dollar rebound.
On the other hand, the trend in oil prices in the United States is still high. Although gasoline prices have fallen in the past two weeks, this has not changed the situation of escalating crude oil prices. The Biden administration wants to cool oil prices by banning exports and suspending gasoline taxes. However, the current global situation of tight energy supply is pushing oil prices higher, coupled with sanctions against Russia, which continue to support higher oil prices. Reducing inflation over the short term is challenging since cooling oil prices is hard when there is an imbalance between supply and demand. This will help maintain the expectation of interest rate hikes. Still, the amplitude will also be constrained by economic data.
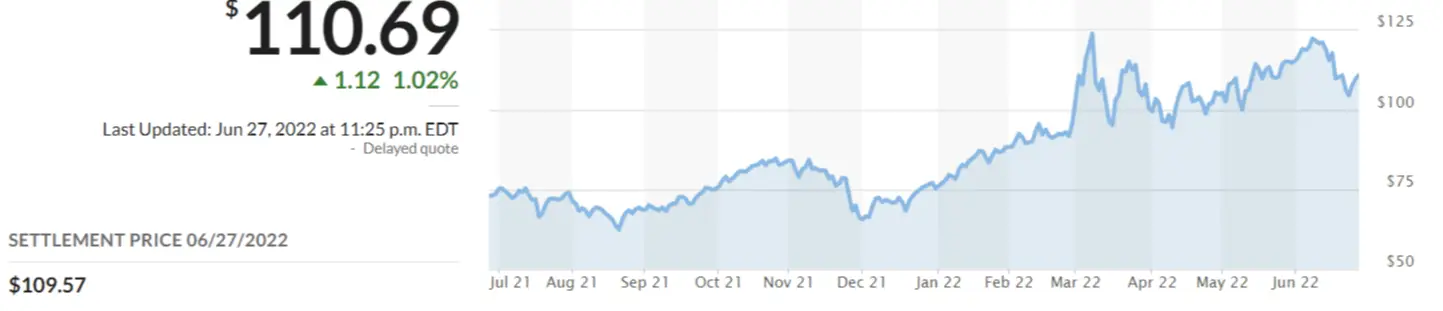
Uncertainty regarding the dollar highlights the importance of monitoring if an interest rate hike could be adjusted due to changes in economic data. The high significance of the GDP data for the first and second quarters and the data from various segments to assess whether the US economy will fall into recession cannot be overstressed. However, the current economic downturn forecast is not conducive to boosting the stock market, which continues to be sluggish. Comments by crucial Fed officials reflect their position on interest rate hikes, with many being hawkish. Changes in market sentiment and whether they can bring some rebound momentum to the stock market can be identified from observing such patterns.


